The Unpredictability of Climate Models
Modern climate science relies heavily on advanced computational models to project future climate trends. These models integrate vast datasets, analyzing everything from ocean currents to atmospheric pressure. Organizations and researchers around the world contribute to this effort, with initiatives such as climateprediction.net playing a role in expanding computational power for climate simulations. Despite technological advancements, the increasing complexity of climate change presents significant challenges in predicting future weather patterns with precision.
The Acceleration of Global Warming
Scientific evidence shows that global temperatures have been rising at an alarming rate. The past decade has been the warmest on record, with extreme weather events occurring more frequently. From devastating hurricanes to prolonged droughts, climate change is no longer a distant concern but an immediate crisis.
Rising carbon dioxide levels, largely due to human activities, are the primary driver of this warming trend. Industrial emissions, deforestation, and extensive fossil fuel consumption continue to release greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, trapping heat and disrupting the Earth’s delicate climate balance. As a result, regions around the world are experiencing record-breaking heatwaves and shifting weather patterns that threaten ecosystems and human livelihoods.
The Role of Melting Polar Ice
One of the most visible consequences of global warming is the rapid melting of polar ice. Satellite imagery reveals that Arctic sea ice has been shrinking at an unprecedented rate, leading to rising sea levels and increased coastal flooding. In Antarctica, massive ice shelves are breaking apart, releasing billions of tons of freshwater into the ocean.
Melting polar ice not only contributes to rising sea levels but also alters ocean currents. The influx of freshwater from ice sheets disrupts the thermohaline circulation, a crucial component of global climate regulation. If these disruptions continue, weather patterns could become even more erratic, with some regions experiencing more severe storms while others face prolonged droughts.
The Impact on Agriculture and Food Security
Climate change is placing immense pressure on global agriculture. Rising temperatures, shifting precipitation patterns, and increased frequency of extreme weather events are making it difficult for farmers to maintain stable crop yields. In some regions, prolonged droughts have decimated harvests, leading to food shortages and economic instability.
Changing climates also facilitate the spread of pests and plant diseases, further threatening food production. Warmer temperatures create favorable conditions for invasive species that damage crops and reduce yields. As food security becomes more uncertain, communities around the world must adapt by developing resilient agricultural practices and investing in sustainable farming techniques.
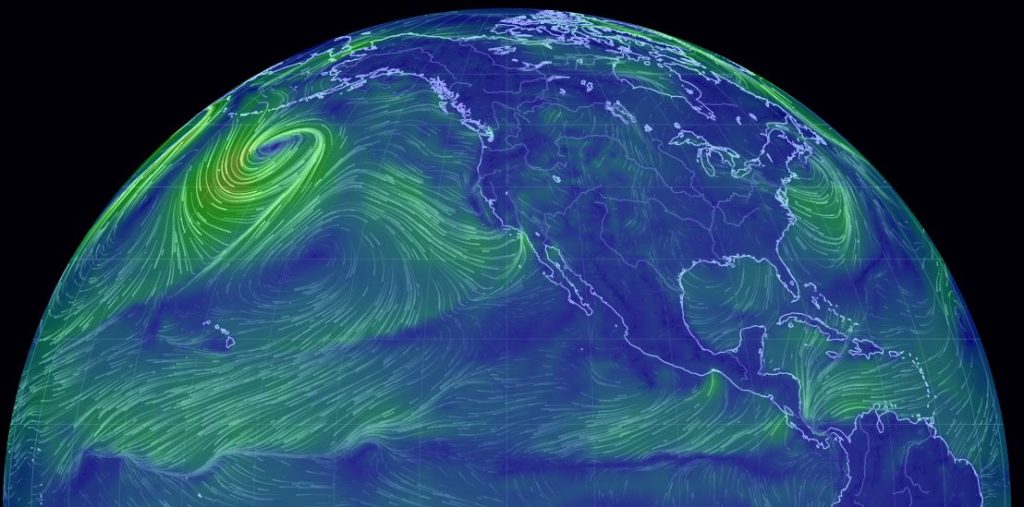
The Growing Threat of Extreme Weather Events
Hurricanes, wildfires, and floods are becoming more intense due to the warming climate. The frequency and severity of these disasters have increased, leaving communities struggling to recover from repeated devastation. Coastal cities face heightened risks as rising sea levels amplify storm surges, causing widespread destruction and displacement.
In many cases, infrastructure is not designed to withstand the new climate reality. Aging flood control systems, outdated building codes, and inadequate emergency response plans make cities vulnerable to climate-related disasters. Governments and policymakers must take urgent action to strengthen resilience and implement strategies that mitigate the impact of extreme weather.
The Influence of Climate Change on Migration Patterns
As environmental conditions become harsher, climate-induced migration is on the rise. Millions of people are being forced to leave their homes due to rising sea levels, desertification, and extreme weather events. Low-lying island nations face existential threats, with entire communities at risk of being submerged by rising waters.
In many parts of the world, climate refugees face uncertain futures as they seek safer living conditions. The growing displacement crisis demands international cooperation to address the humanitarian challenges posed by climate-induced migration. Without coordinated action, conflicts over resources and territory could escalate, further complicating the global response to climate change.
The Economic Costs of Inaction
The financial consequences of climate change are staggering. The cost of rebuilding after natural disasters, loss of agricultural productivity, and healthcare expenses due to climate-related illnesses place an enormous burden on economies. Insurance companies are already adjusting their policies to account for the rising risks associated with extreme weather, driving up costs for homeowners and businesses.
A lack of investment in climate resilience and sustainable infrastructure will only exacerbate these financial challenges. Governments and industries must recognize the long-term benefits of proactive climate policies, including investments in renewable energy, carbon reduction initiatives, and climate adaptation strategies.
The Shift Towards Renewable Energy
Transitioning to clean energy sources is one of the most effective ways to combat climate change. Solar, wind, and hydropower technologies have advanced significantly, making renewable energy more accessible and cost-effective. Countries that invest in green energy not only reduce their carbon footprint but also create new job opportunities and stimulate economic growth.
The shift away from fossil fuels, however, faces political and economic hurdles. Fossil fuel industries wield significant influence, and resistance to change remains strong in certain regions. Governments must implement policies that encourage the adoption of renewable energy while providing support for communities transitioning away from fossil fuel dependence.
The Importance of Global Cooperation
Climate change is a global crisis that requires a unified response. International agreements such as the Paris Agreement aim to set emissions reduction targets and encourage sustainable development. While progress has been made, some countries continue to lag behind in their commitments to reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
Diplomatic efforts must prioritize climate action, ensuring that wealthier nations support developing countries in their transition to greener economies. Climate finance initiatives, technology transfers, and knowledge-sharing programs can help build a more sustainable future for all nations.
The Role of Individuals in Addressing Climate Change
While governments and industries play a significant role in climate mitigation, individual actions also contribute to meaningful change. Reducing energy consumption, supporting sustainable businesses, and advocating for environmental policies can make a difference. Public awareness and grassroots movements have the power to push policymakers toward stronger climate commitments.
Consumer choices, such as reducing plastic waste, adopting plant-based diets, and using energy-efficient appliances, collectively influence market trends and encourage companies to adopt more sustainable practices. Individual efforts, when combined with systemic change, can accelerate the fight against climate change.
The Future of Climate Science and Innovation
Scientific advancements continue to enhance our understanding of climate change and potential solutions. Innovations in carbon capture, geoengineering, and sustainable technology offer promising avenues for reducing environmental impact. Research institutions and private enterprises are exploring ways to mitigate emissions while ensuring economic viability.
Artificial intelligence and machine learning are also playing a role in climate research, improving climate models and enabling more accurate predictions. Enhanced data analysis helps scientists develop targeted strategies for adaptation and mitigation, increasing the effectiveness of climate policies.
A Critical Moment for Action
The consequences of climate change are already being felt worldwide, and the urgency for action has never been greater. Governments, industries, and individuals must work together to implement meaningful solutions that address the root causes of climate change. The choices made today will determine the future stability of the planet, making it imperative to prioritize sustainability and resilience.
Failure to act will result in irreversible damage to ecosystems, economies, and communities. The scientific evidence is clear, and the time for decisive action is now. By embracing renewable energy, strengthening climate policies, and fostering global cooperation, humanity can navigate the challenges of a changing climate and build a more sustainable world.